Water is the lifeblood of any garden, yet with increasing environmental concerns and unpredictable weather patterns, conserving this precious resource has never been more critical. Whether you’re nurturing your first potted herb or managing a lush landscape, understanding creative water-saving techniques can transform your gardening practices and contribute positively to the planet.
In this article, you’ll discover twelve innovative methods that not only reduce your water usage but also enhance plant health and garden productivity. From selecting drought-tolerant plants to mastering the art of efficient irrigation, these techniques blend traditional wisdom with modern insights, offering something valuable for gardeners at every skill level.
By the end of your read, you’ll be equipped with practical strategies to maintain a thriving garden, even in the driest of times. These approaches will empower you to garden more sustainably, ensuring your green oasis continues to flourish while respecting our shared environment. Let’s embark on this journey together and explore how simple changes can make a significant difference in your garden and beyond.
Install Drip Irrigation Systems
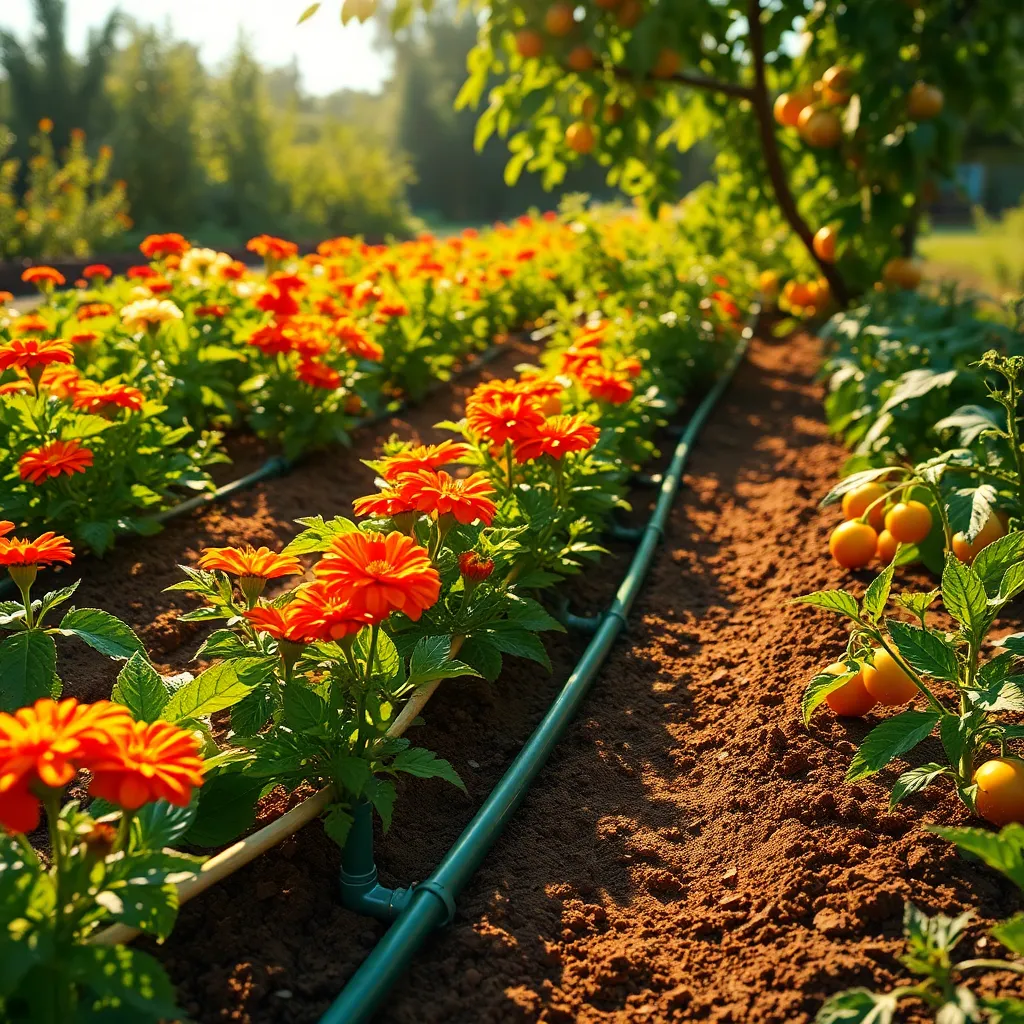

Drip irrigation systems offer an efficient way to water plants by delivering moisture directly to the roots. This method minimizes water waste and ensures that your garden thrives even in dry conditions.
For beginners, installing a drip irrigation system might seem daunting, but it can be quite straightforward. Start by planning the layout: measure your garden and determine the best placement for hoses and emitters to cover all plants.
Use a timer with your drip irrigation to automate watering schedules, ensuring consistency. Adjust watering times seasonally, as plants often need less water during cooler months.
Advanced gardeners can benefit from customizing their systems with different types of emitters for varied plant needs. For instance, use micro-sprayers for broad coverage of leafy vegetables and drip emitters for precise watering of individual plants like tomatoes.
Mulch Heavily Around Plants
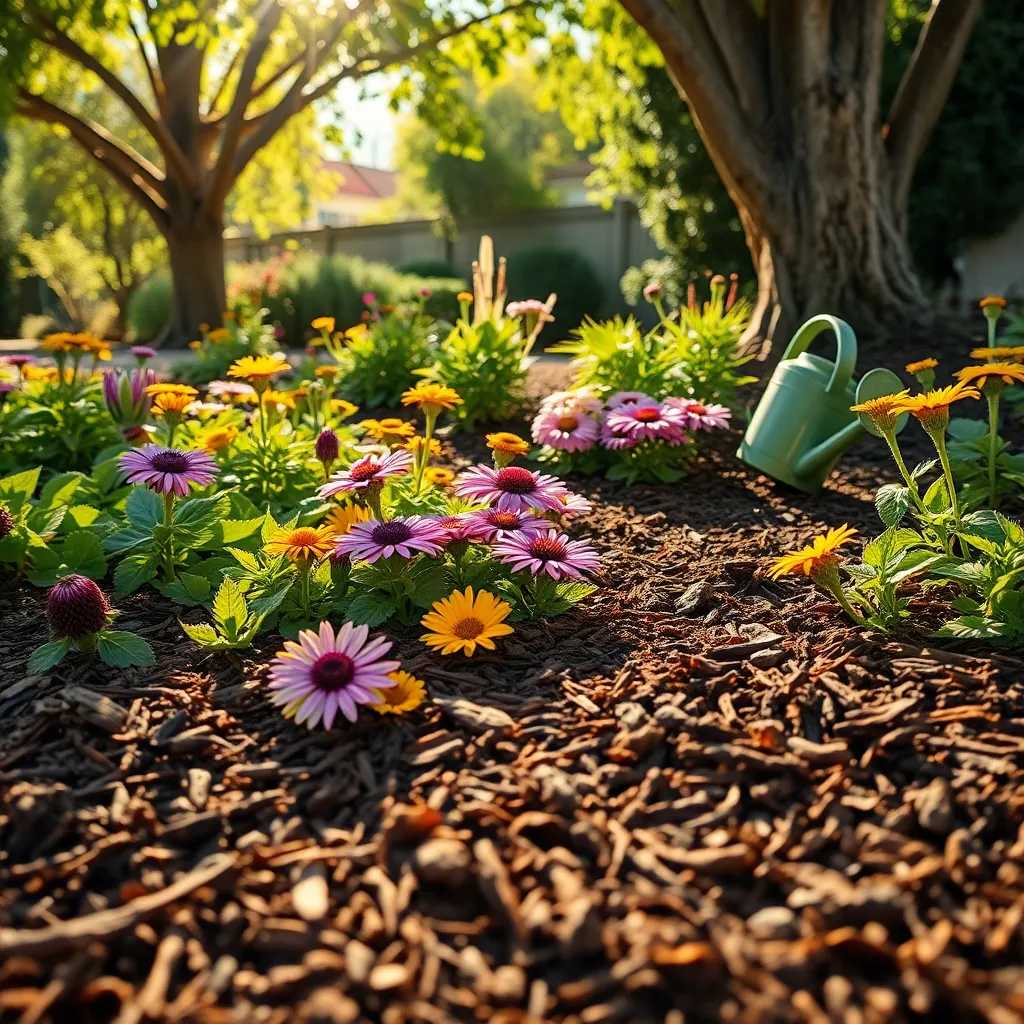

Mulching heavily around plants is an excellent way to conserve water in your garden. By adding a thick layer of mulch, you can significantly reduce evaporation and maintain soil moisture levels.
Firstly, choose the right type of mulch for your plants, such as organic options like bark, straw, or shredded leaves. These materials not only help in conserving water but also improve soil health as they decompose over time.
Apply a layer of mulch that is about 2 to 4 inches thick, ensuring it covers the soil completely but does not touch the plant stems. This thickness is crucial because it provides enough insulation to keep the soil cool and reduce water loss.
For more advanced gardeners, consider using a combination of mulch types to maximize benefits. For instance, you can use a layer of straw for insulation topped with bark chips for aesthetic appeal and long-term moisture retention.
Collect Rainwater in Barrels
Collecting rainwater in barrels is a simple yet effective way to conserve water for your garden. Not only does this practice reduce your water bill, but it also provides your plants with naturally soft water, free of chemicals like chlorine and fluoride.
Begin by choosing a sturdy barrel, ideally one made from food-grade plastic, which won’t leach harmful substances into the water. Position it under a downspout to maximize water collection, ensuring it has a secure lid to prevent debris and insects from contaminating the water.
For those living in areas with frequent rainfall, installing multiple barrels linked together can significantly increase your water storage capacity. Consider adding a spigot near the bottom of the barrel for easy access to the water, making it convenient to fill watering cans or attach a hose.
Regular maintenance is key to keeping your rainwater system efficient and healthy. Clean the barrels periodically to prevent algae growth and ensure the gutters feeding them are free from leaves and debris.
Use Greywater for Irrigation
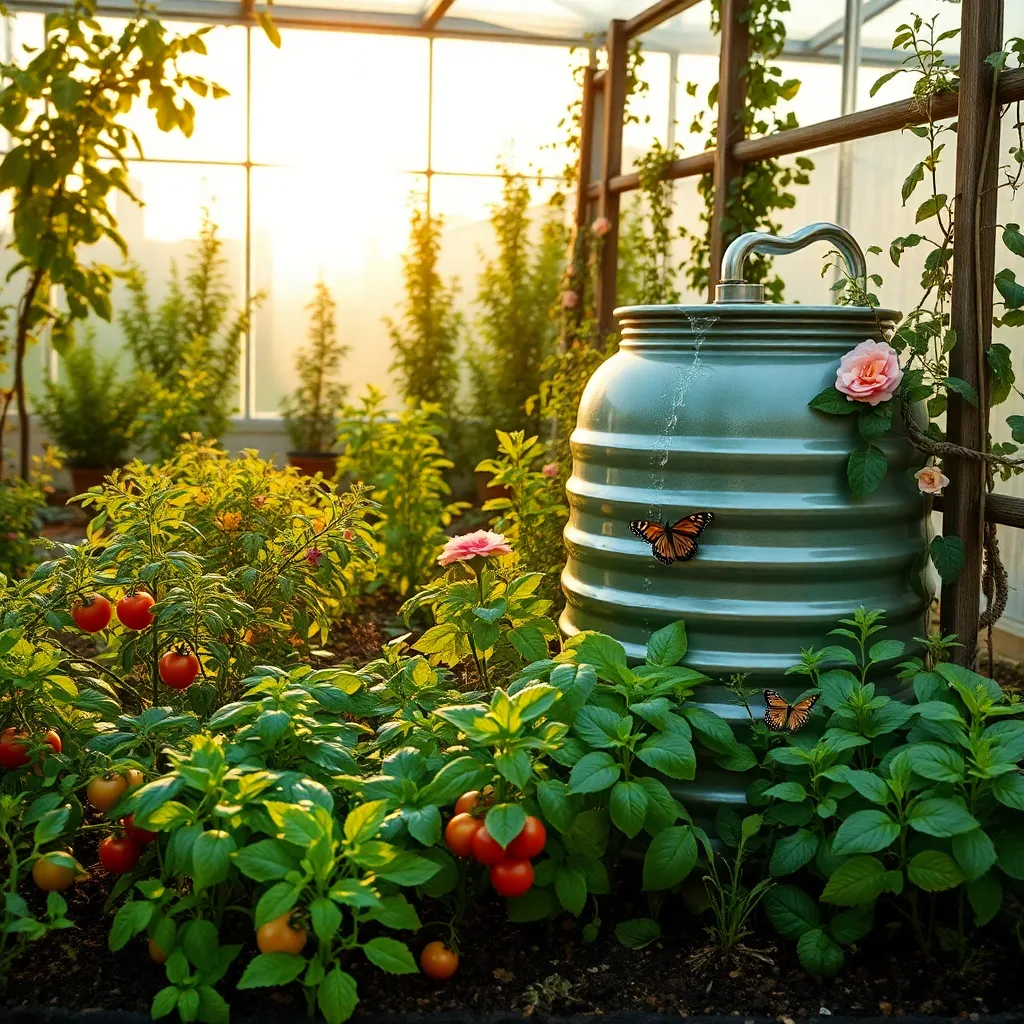

Greywater, which is wastewater from baths, sinks, and washing machines, can be an excellent resource for garden irrigation. By reusing greywater, gardeners can significantly reduce their water usage, making their gardens more sustainable and eco-friendly.
Before using greywater, consider the types of soap and detergents you use, as some can be harmful to plants. Opt for biodegradable and eco-friendly products to ensure that your greywater is safe for your garden.
It’s essential to use greywater on ornamental plants and trees rather than edible crops unless you have a system that filters the water thoroughly. This precaution helps prevent potential contaminants from entering your food supply.
Advanced gardeners can set up a greywater irrigation system that automatically distributes water to their plants. Such systems can be customized to direct water to specific areas, ensuring that only the plants that need it receive this valuable resource.
Plant Drought-Resistant Varieties
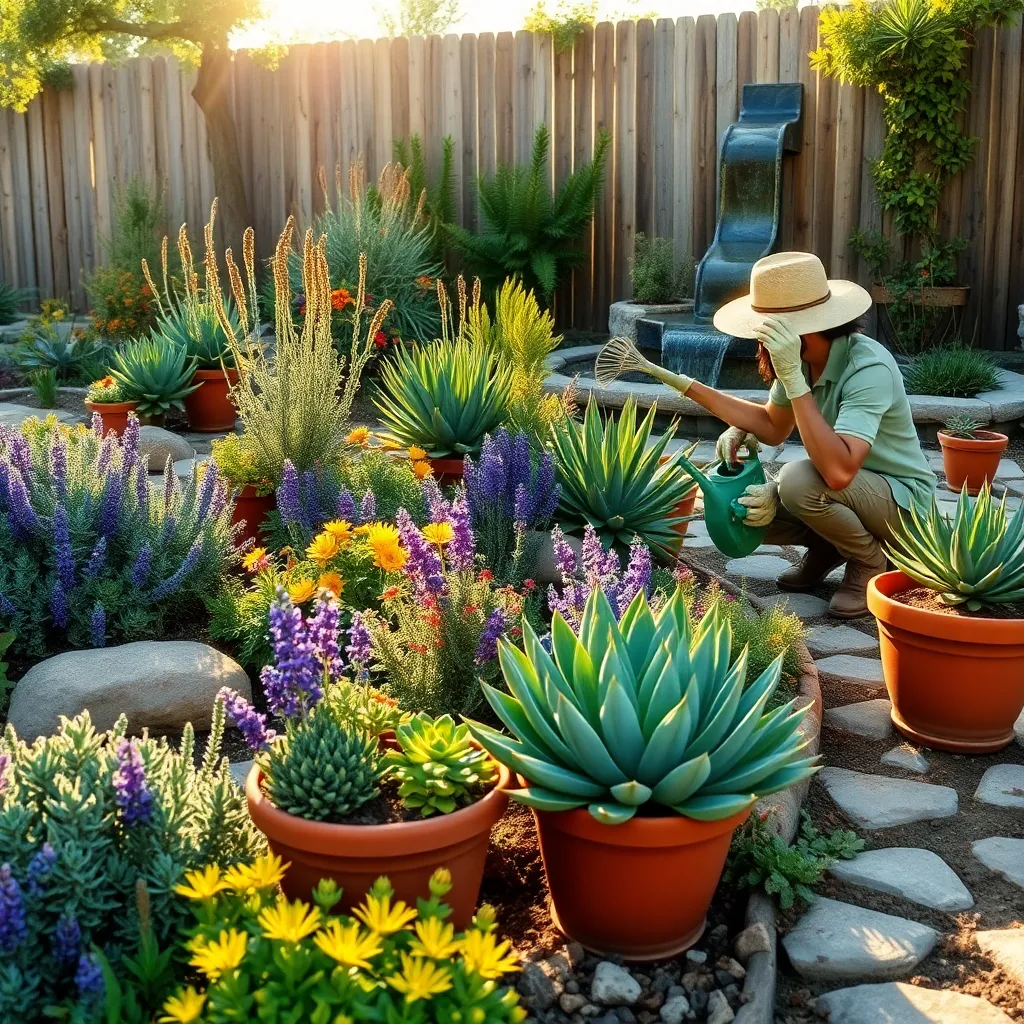

Consider planting drought-resistant varieties to conserve water effectively in your garden. These plants are adapted to thrive with minimal irrigation, making them an excellent choice for water-conscious gardeners.
When selecting drought-tolerant plants, look for species native to arid regions, as they have evolved to withstand dry conditions. Succulents, lavender, and sage are popular options that require little watering once established.
It’s essential to prepare the soil properly to support these resilient plants. Amend the soil with organic matter like compost to improve water retention and drainage, ensuring your plants have the best start.
For beginners, start with easy-to-grow drought-resistant varieties like yarrow or sedum, which are forgiving and resilient. Experienced gardeners might explore more exotic options such as agave or Russian sage, which add unique textures and colors to the garden.
Water Early Morning or Late

Watering your garden during the early morning or late evening can significantly reduce water loss due to evaporation. This simple adjustment ensures that more moisture reaches the roots, providing better hydration for your plants.
In the coolness of the early morning, your plants can absorb water more efficiently, preparing them for the heat of the day. Watering at this time also helps in preventing diseases that can occur from wet foliage overnight.
Alternatively, late evening watering offers a similar benefit by allowing water to penetrate deeply into the soil with minimal evaporation. Ensure that the foliage dries before nightfall to minimize the risk of fungal diseases.
To optimize your watering routine, consider using a drip irrigation system or soaker hose. These methods deliver water directly to the soil, reducing waste and keeping leaves dry, which is particularly beneficial for plants prone to mildew.
Group Plants by Water Needs

Grouping plants by their water needs is a highly effective strategy for conserving water in your garden. This method ensures that plants with similar moisture requirements are placed together, which prevents overwatering and under-watering.
To start, categorize your plants into three main groups: drought-tolerant, moderate-water, and high-water plants. Drought-tolerant plants, such as lavender and succulents, thrive in well-draining soil and require minimal watering once established.
For plants with moderate water needs, like tomatoes and peppers, aim to water them deeply but less frequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between waterings. This encourages roots to grow deeper, making the plants more resilient to dry periods.
High-water plants, such as ferns and certain tropical species, should be placed in areas where soil retains moisture more effectively, like shaded spots with rich, organic soil. Consider using mulch around these plants to retain soil moisture and reduce evaporation.
Incorporate Water-Retaining Polymers

Water-retaining polymers, often referred to as hydrogels, can be a game-changer for efficient water use in gardens. These granules absorb water and slowly release it, ensuring plants receive a steady supply of moisture without frequent watering.
To incorporate these polymers, mix them directly into the soil at the root level before planting. Use approximately one teaspoon of polymer per gallon of soil for optimal moisture retention, adjusting based on the specific plant’s needs.
For gardeners in dry climates or those with water restrictions, hydrogels provide an excellent way to maintain plant health. They are especially beneficial for container gardening, where soil dries out more quickly.
Experienced gardeners can experiment with varying polymer quantities to match different plant types and soil conditions. Combining polymers with organic mulch can further enhance water retention and improve soil quality over time.
Create Self-Watering Planters

Transforming a traditional planter into a self-watering version is an excellent way to conserve water and reduce maintenance. Begin by selecting a container with a depth of at least 12 inches to accommodate a reservoir and ensure proper root growth.
Next, create a water reservoir at the bottom using a small plastic bottle or a similar container with holes drilled into it. This will allow water to seep into the soil gradually, keeping plant roots moist without overwatering.
To set up your self-watering planter, fill the base with a layer of gravel or small stones to separate the soil from the water reservoir. Then, layer a high-quality potting mix containing organic matter and perlite on top for optimal drainage and nutrient retention.
Incorporate a wicking material, such as a strip of cotton fabric, that extends from the water reservoir to the soil. This will draw moisture up into the soil, keeping it consistently damp and reducing the need for frequent watering.
Practice Deep Soaking Techniques

Deep soaking is a technique where water is applied slowly to allow it to penetrate deeper into the soil, promoting stronger root development. By practicing deep soaking, gardeners can ensure that their plants receive the necessary moisture without frequent watering, which helps conserve water.
To achieve deep soaking, water your garden less frequently but for longer periods. This encourages roots to grow deeper, making plants more resilient to drought conditions and reducing the need for constant watering.
Start by using a soaker hose or drip irrigation system, which can deliver water directly to the soil surface at a controlled rate. Position these tools close to the base of plants to minimize evaporation and maximize water efficiency.
For gardeners with clay or compacted soils, consider adding organic matter like compost to improve water penetration. This will help the soil retain moisture longer and make the most of each deep soaking session.
Employ Shade Cloth on Hot Days
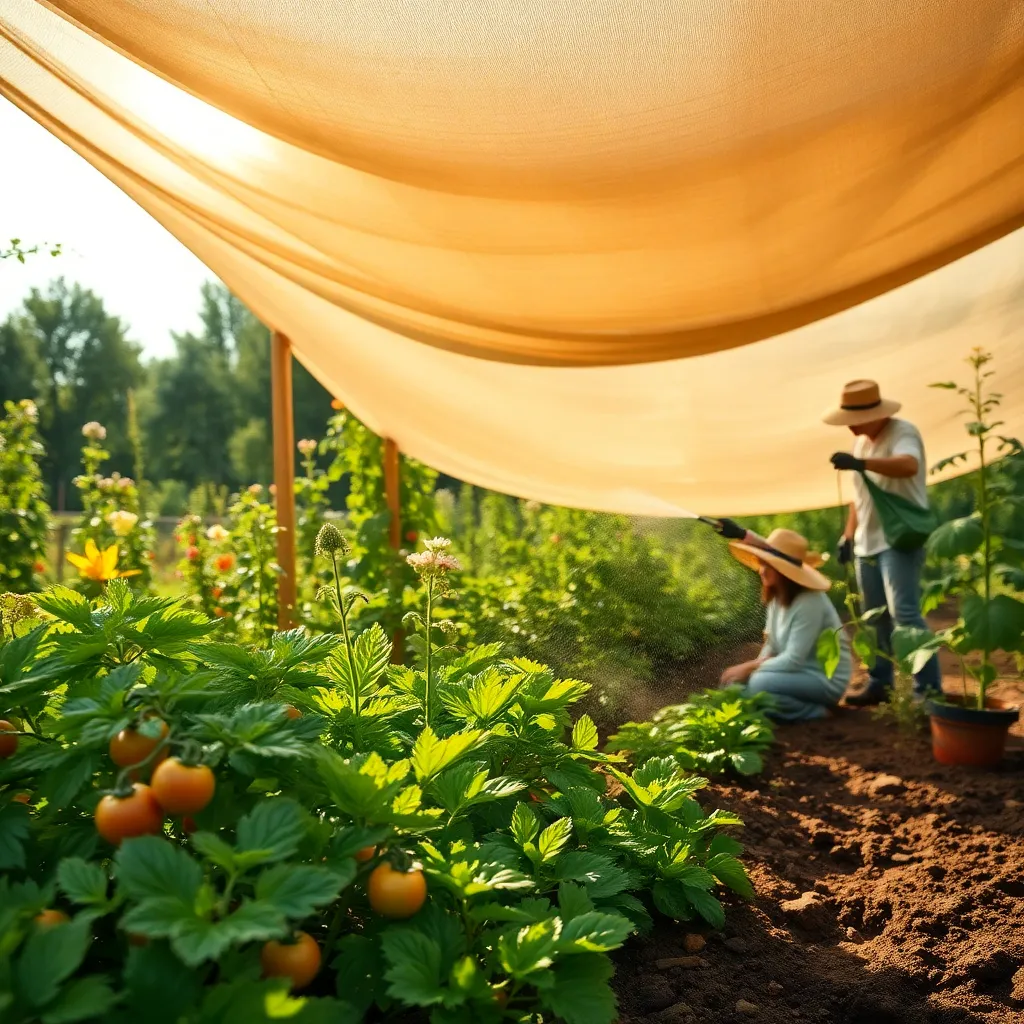

When the summer heat becomes relentless, employing shade cloth can be an effective way to protect your plants and conserve water. Shade cloth reduces the amount of direct sunlight reaching your plants, minimizing evaporation and helping to retain moisture in the soil.
For most gardens, a shade cloth with a 30% to 50% density is sufficient to shield plants from intense sun without compromising their growth. Choose a breathable fabric that allows air circulation while providing adequate shade to prevent overheating.
Setting up a shade cloth is simple; you can drape it over a structure, such as a pergola, or use stakes to create a tent-like cover over your plants. Ensure the cloth is securely fastened to withstand wind, and adjust the height as needed to allow for plant growth and easy access.
Advanced gardeners might consider using adjustable shade cloth systems that can be retracted or extended depending on the weather. This flexibility not only protects plants on extremely hot days but also allows them to receive ample sunlight when temperatures are cooler. Experimenting with different densities and setups can help you find the perfect balance for your specific garden needs.
Regularly Check for Leaks

Regular maintenance of your garden’s watering system can significantly save water. Checking for leaks ensures that every drop of water is used efficiently, preventing waste and reducing your water bill.
Begin by inspecting all hoses, connectors, and irrigation systems for any signs of wear or damage. Even a small leak can waste gallons of water over time, so it’s crucial to address issues promptly.
For those using drip irrigation, make sure that emitters are not clogged or broken. A well-maintained drip system delivers water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
Advanced gardeners might consider installing a water pressure regulator to prevent leaks caused by excessive pressure. This simple device can extend the life of your irrigation system and improve its efficiency.
Conclusion: Growing Success with These Plants
In nurturing thriving relationships, just as in cultivating a garden, creativity and care are key. We’ve explored 12 innovative techniques to conserve resources and nourish growth, such as fostering open communication, setting healthy boundaries, practicing gratitude, and embracing change. Other concepts include nurturing shared interests, managing conflicts with empathy, and prioritizing quality time together. These strategies, akin to water-saving in gardens, ensure relationships flourish even in challenging times.
As an immediate next step, choose one technique from this article to implement today—perhaps initiating a heartfelt conversation or planning a small gesture of appreciation. Taking this small action could be the catalyst for deeper connection and understanding.
Remember, relationship growth is a journey. Bookmark this article to revisit these techniques whenever you need guidance or inspiration. As you apply these principles, you are laying the foundation for enduring success and fulfillment in your relationships. Embrace the process with patience and optimism, knowing that every effort you make today is investing in a brighter, more harmonious tomorrow. Save this article now, and take the first step towards a flourishing relationship garden.



